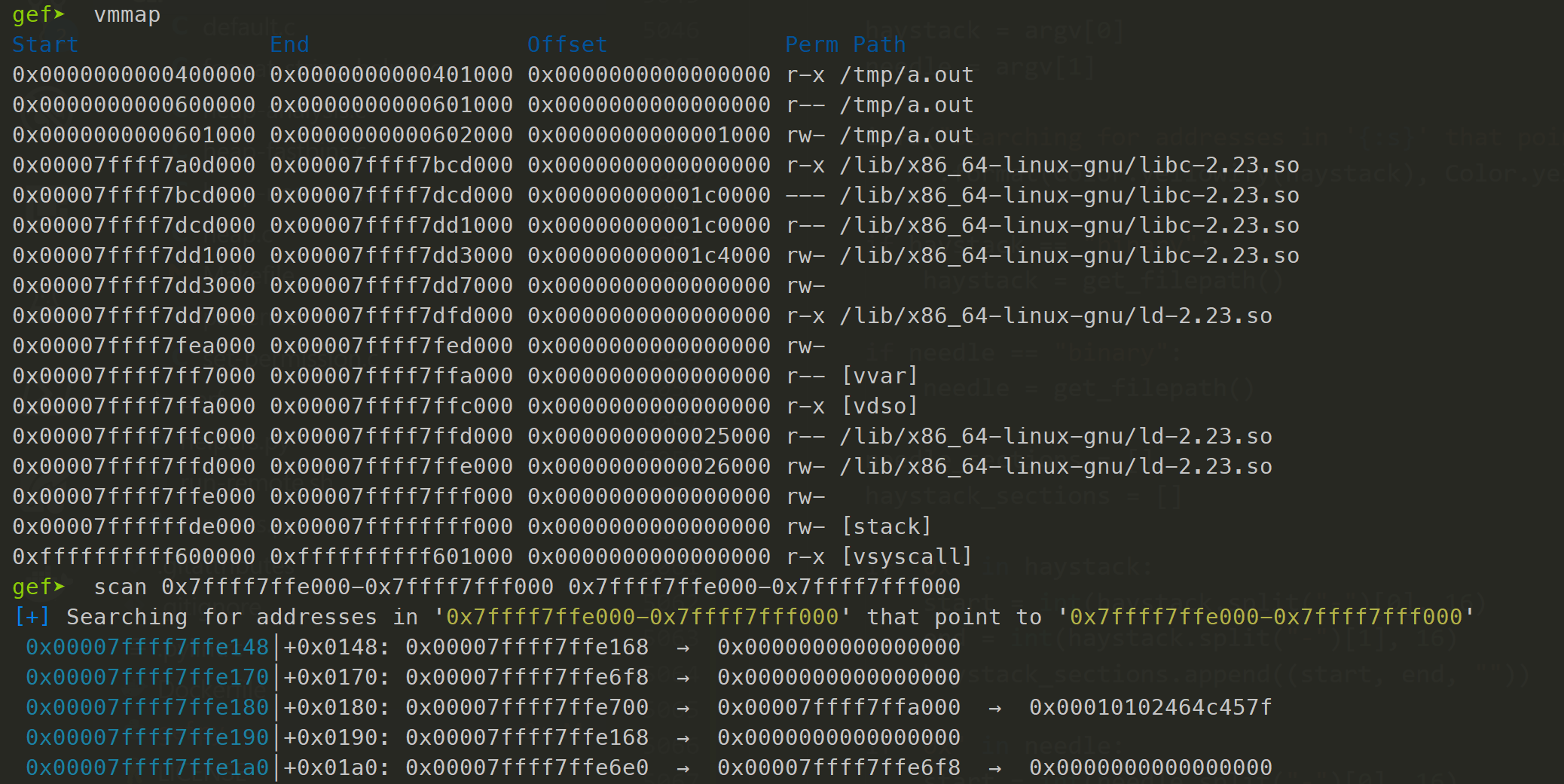
scan
Command scan
scan searches for addresses of one memory region (needle) inside another region (haystack) and
lists all results.
Usage:
gef➤ scan NEEDLE HAYSTACK
scan requires two arguments, the first is the memory section that will be searched and the second
is what will be searched for. The arguments are grepped against the process's memory mappings (just
like vmmap) to determine the memory ranges to search.
gef➤ scan stack libc
[+] Searching for addresses in 'stack' that point to 'libc'
[stack]: 0x00007fffffffd6a8│+0x1f6a8: 0x00007ffff77cf482 → "__tunable_get_val"
[stack]: 0x00007fffffffd6b0│+0x1f6b0: 0x00007ffff77bff78 → 0x0000001200001ab2
[stack]: 0x00007fffffffd758│+0x1f758: 0x00007ffff77cd9d0 → 0x6c5f755f72647800
[stack]: 0x00007fffffffd778│+0x1f778: 0x00007ffff77bda6c → 0x0000090900000907
[stack]: 0x00007fffffffd7d8│+0x1f7d8: 0x00007ffff77cd9d0 → 0x6c5f755f72647800
[...]
Advanced Needle/Haystack syntax
To check mappings without a path associated, an address range (start-end) can be used. Note that ranges don't include whitespaces.